集成开发环境-GCC.ARM(#02)程序构建
倘若只有 main.h 和 main.c 两个文件,那么只需要执行少量的指令即可完成编译工作。但是实际上一个工程通常包含几十上百个文件,意味着要执行大量的编译指令才能得到目标文件,这是我们所无法接受的。因此需要借助 make、cmake、ninja、scons 等构建工具来提高开发效率。
make
在 windows 系统中推荐使用 MSYS2 提供的 mingw32-make 程序。
生成脚本(makefile)
相较于头开始写 makefile 脚本,先通过 STM32CubeMX 生成然后加以改造则要容易得多。
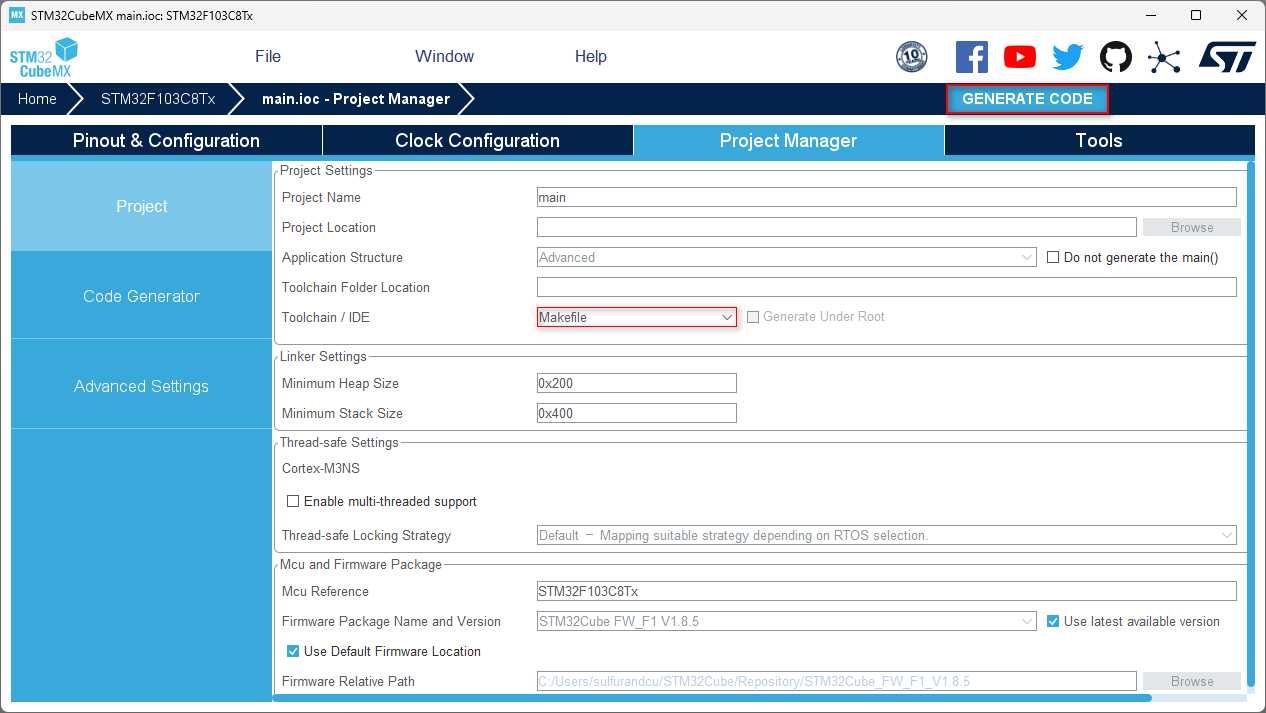
修改脚本(makefile)
- 修改文件列表(*.c & *.s)
C_SOURCES = \
../../../code/Application/src/main.c \
...ASM_SOURCES = \
startup_stm32f103xb.s \
... - 修改包含路径(*.h)
C_INCLUDES = \
-I../../../code/Application \
... - 修改全局定义(#define)
C_DEFS = \
-DUSE_HAL_DRIVER \
-DSTM32F103xB \
... - 修改链接脚本(.ld)
LDSCRIPT = STM32F103C8Tx_FLASH.ld
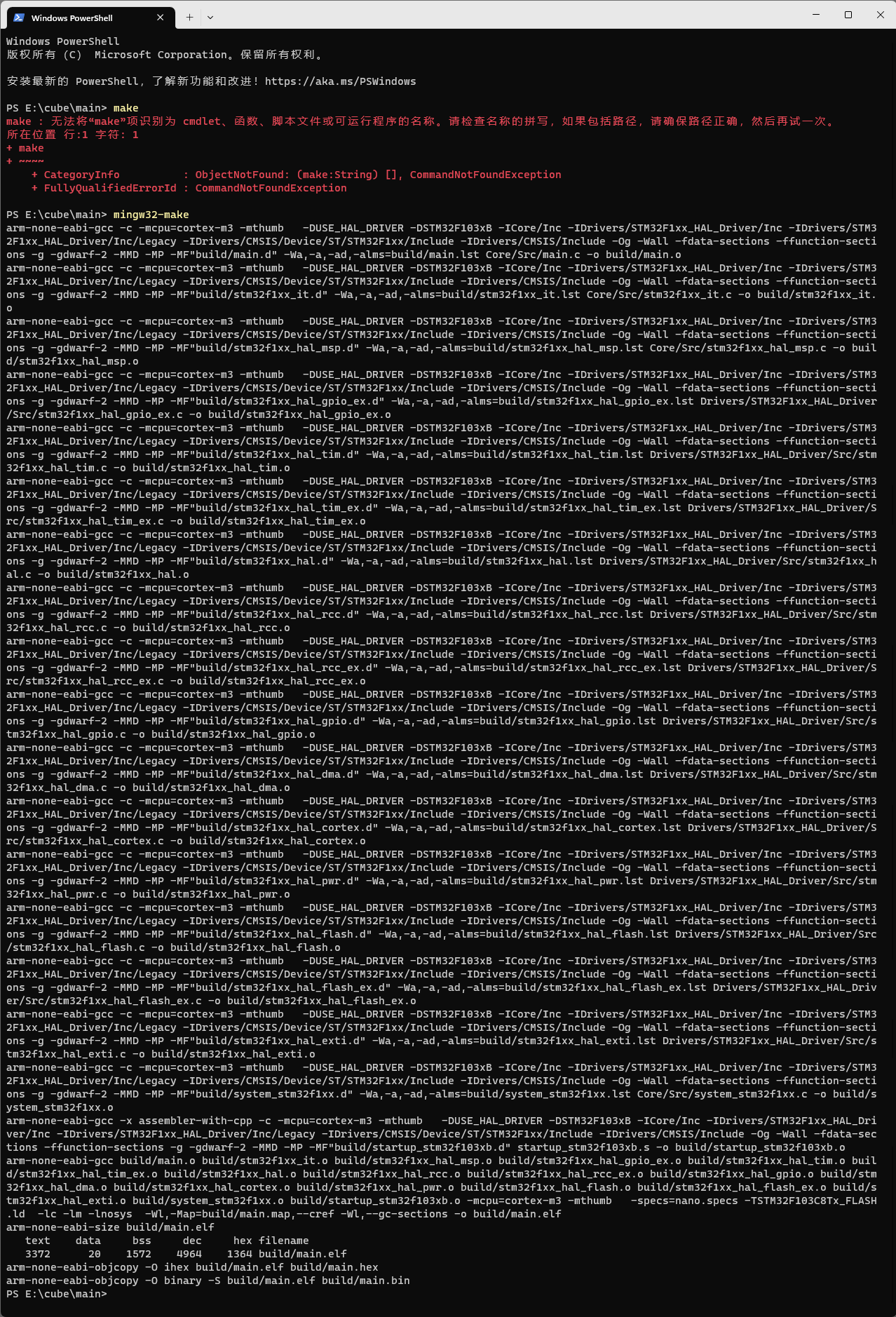
执行编译
在 makefile 所在的路径下执行 make 指令开始编译
清除编译
若要清除刚才编译的中间文件,则需要修改 makefile 文件,然后执行 mingw32-make clean 指令。
clean: |
这时你大概率会遇到以下问题:
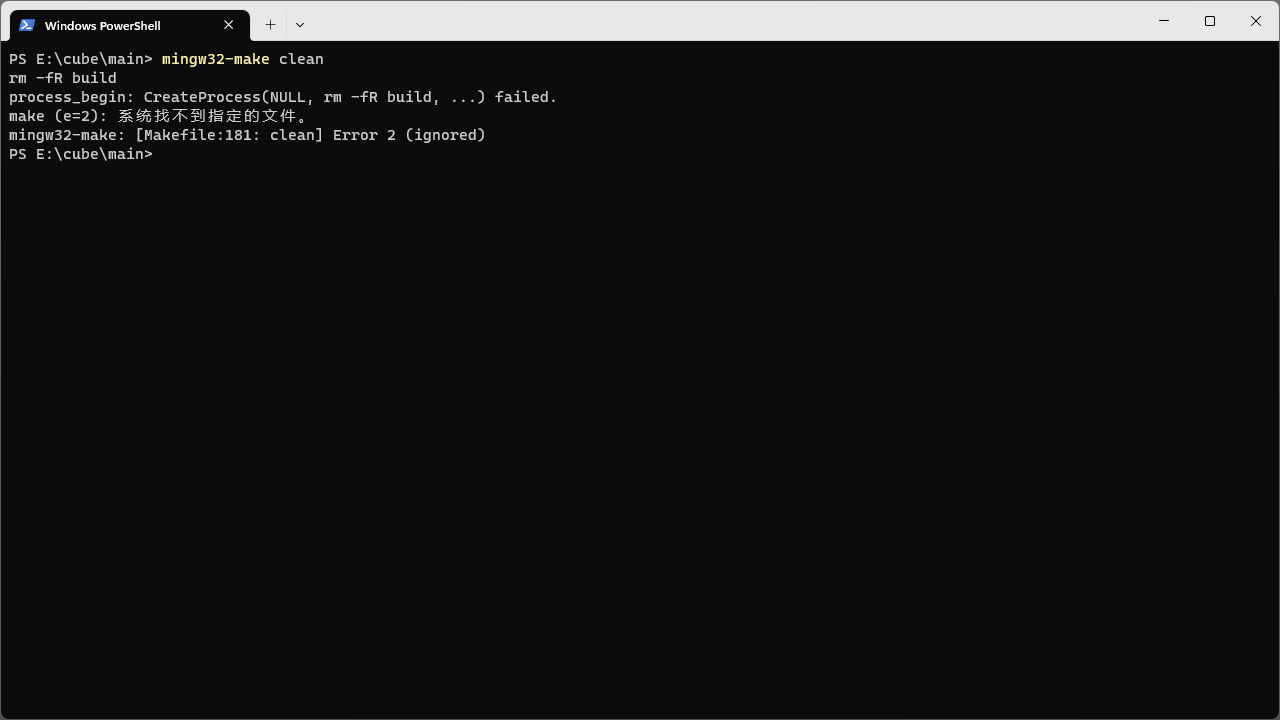
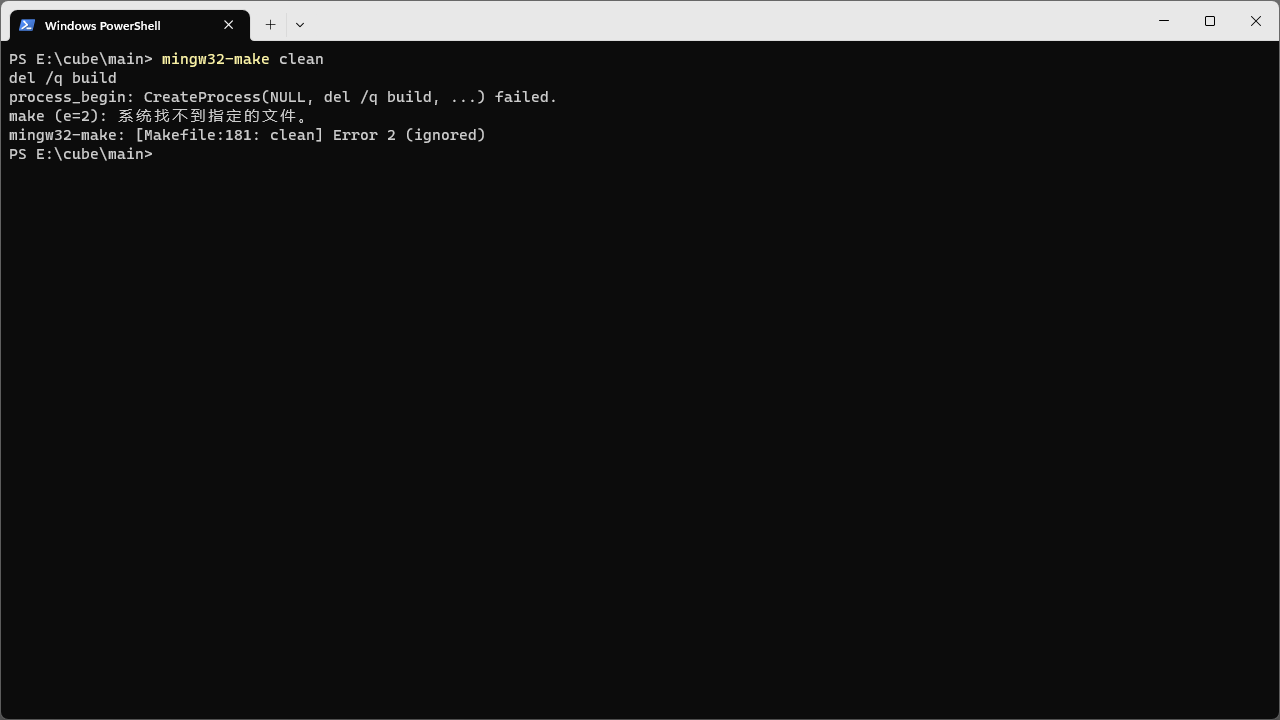
有人说将 clean 下的 -rm -fR $(BUILD_DIR) 改成 -del /q $(BUILD_DIR) 就好了,实测并不管用。
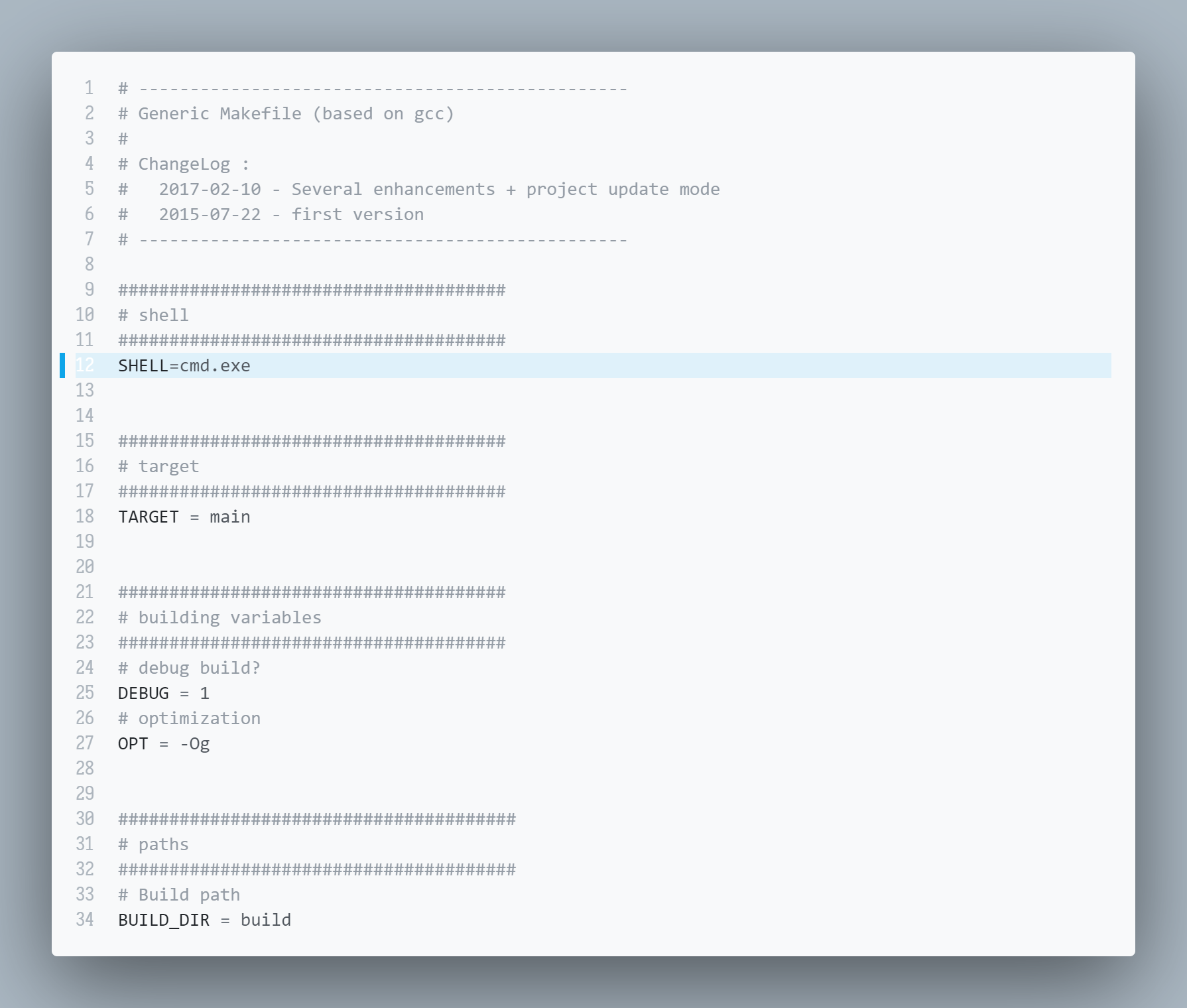
只有显式地将 SHELL 指定为 cmd 才行(在 makefile 中添加一条语句):
scons
- install python
- install pip (python get-pip.py)
- install scons (python -m pip install scons==3.1.2)
- install pywin32 (support scons -j16) (python -m pip install pywin32)
python/Scripts/scons.bat # scons.bat is not necessary, just run scons directly. |
$ scons.bat
scons: Reading SConscript files …###############################
SConstruct enter !!!.#######################################
SDK_ROOT: E:\codespace\SPL1050\SPL1050V240112_vendor-Release_1.0.0.1_modified
SConstruct building start !!!
SConstruct exit !!!.#######################################
scons: done reading SConscript files.#######################################
scons: Building targets …
scons: building associated VariantDir targets: build\gcc\obj
LINK rtthread.elf
Memory region Used Size Region Size %age Used
FalPartRAM: 1504 B 4 KB 36.72%
ROM: 384448 B 380 KB 98.80%
RAM: 200456 B 256 KB 76.47%
Heap_RAM: 0 GB 127 KB 0.00%
FalPartTableInFlash: 1504 B 4 KB 36.72%
CopyTable: 20 B 1 KB 1.95%
CodeInFlash: 492096 B 768 KB 62.57%
phycfg: 0 GB 4 KB 0.00%
arm-none-eabi-size rtthread.elf
text data bss dec hex filename
878048 8540 191936 1078524 1074fc rtthread.elf
arm-none-eabi-objcopy -O ihex rtthread.elf ./build/gcc/bin/rtthread.hex
scons: done building targets.
env 中突然不能编译的问题
使用自己安装的 scons.bat 编译后,再用 env 中的 scons 编译有可能会报错,删除 .sconsign.dblite 后再编即可。
交叉编译工具链的路径问题
多人开发时,每个人的交叉编译工具链的安装位置都不同,这样就不能把绝对路径写入到 rtconfig.py 中并提交至代码仓库。既然绝对路径不行,那相对路径可以吗?也行不通,使用相对路径意味着交叉编译工具链也要同步提交至代码仓库,而 arm-none-eabi 的体积是比较大的,所以说我们通常不会这么做,那应该怎样优雅地解决这个问题呢?请继续往下看:
只需要在 rtconfig.py 中添加以下代码即可解决!
import configparser |
其逻辑为:
1. 检查 rtconfig.ini 是否存在。
2. 如果不存在则自动创建一个 rtconfig.ini 模板文件,并提醒开发人员进行修改。
3. 如果存在则从中提取交叉编译工具链的路径信息。
下面是自动生成的 rtconfig.ini 模板
# do not commit this file to the repository. |